What is Fiber Optic Splice Closure?
Fiber Optic Splice Closure, also called Fiber Enclosures or FOSC. It is a vital component of fiber optic networks that are used to protect and organize fiber optic cables, which is the best equipment for the fiber management system allowing splicing and passive component integration in the external network. Usually, Fiber Optic Closure accommodates various splice applications such as express, branch, or drop. There are two types of specifications for fiber optic closure. One is Dome Fiber Optic Splice Closure, and the other is Horizontal Fiber Closure.
What is the function of Fiber Optic Splice Closure?
Optical networks rely on the seamless transmission of fiber signals through fiber optic cables. Fiber optic splices are created when two fiber strands are joined, either temporarily or permanently. These connections are sensitive to environmental factors like moisture, dust, and temperature fluctuations, which can degrade fiber signal quality, causing network failures or decreased performance. Optical Fiber Closure addresses these challenges by providing a robust, sealed, and organized environment for housing splices, ensuring network longevity and high performance.
What are the Components of a Fiber Optic Splice Closure?
FOSC consists of several key components, each contributing to its overall effectiveness in protecting and organizing fiber optic splices:
A. Body Housing: The outer shell, typically made from a polymer, ribbed for extra strength, provides mechanical protection against environmental factors like impact, UV radiation, and chemical exposure.
B. Sealing system: Gaskets, o-rings, or gel-based seals prevent contaminants from entering the enclosure and ensure that splices remain clean and dry, maintaining optimal signal transmission conditions.
C. Splice tray: The function of the Splice Tray organizes, secures, and protects every fiber and its splices, simplifying maintenance and future upgrades, and reducing the risk of fiber damage during handling.
D. Storage Baskets: The function of the Storage Baskets store redundant optical cables to avoid the disorder of redundant optical cables affecting the transmission of optical fiber data.
E. Cable entry ports: These enable fiber optic cables to pass through the closure while maintaining the enclosure's integrity, accommodating various cable sizes and types.
F. Cable Strength Member Fixation Point: The central strength member of each individual cable can be attached at this point to prevent fiber damage due to stress or tension.
G. Grounding: A sealed grounding feed-through bolt can be pre-installed in the fiber optic splice box to connect metallic components to an external ground, reducing electrical hazards and protecting against potential lightning strikes or power surges (Optical).
H. Air Valve: The Air Valve is pre-installed in the dome closure if pressure access is required (Optional).
Dome Closure Characteristic:
One of the most commonly used FOSCs is Dome Closure, the max capacity holds up to 576 fibers. Have Heat-Shrinkable Sealing & Mechanical sealing 2 different cable sealing technology. It is usually used for Aerial, Underground, and Pole Mounting applications. Dome Fiber Enclosure features an O-ring sealing system along with an innovative latching/Locking mechanism. This combination is designed to allow simple, watertight closure. utilizes heat-shrinkable technology for cable sealing to make FOSC protective level comply with IP68.
Dome Fiber Closure adopts Tap-off splices are those where most of the fibers in a cable are “expressed” uncut through the closure and only a few fibers are cut and re-spliced to feed a building or Optical Network Unit (ONU), which provides a compact solution for the Fiber-To-The-Home (FTTH) market.

Horizontal Closure Characteristic:
The horizontal closure is larger and the max capacity can hold up to 288 fibers. It is mostly used for Aerial, Underground, and Manhole applications. FOSC supports mechanical sealing with an innovative latching mechanism allowing for easy access during maintenance and repair. Mechanical Sealing technology for cable sealing to make FOSC protective level comply with IP68.

Fiber optic splice closures are used in various applications, including telecommunications, data centers, and FTTH networks. They protect fiber optic cables from environmental factors such as moisture, dirt, and other contaminants that could affect their performance. FOSC plays a vital role in ensuring reliable and high-quality fiber optic communication.
What are the FOSC’s Applications?
Fiber Optic Splice Closures are widely used in many industries and applications, showcasing their versatility and importance in modern communication networks:
A. Telecommunications: Fiber enclosures are essential for protecting splices in long-haul, metropolitan, and access networks, where signal integrity and reliability are critical to providing seamless communication services.
B. CATV: Fiber Enclosure safeguards connections in CATV networks, ensuring high-quality video and data transmission for subscribers.
C. Data Centers: Fiber Optic Closure protects splices in local area networks (LANs), and enterprise networks, where high-speed data transmission and low latency are crucial for maintaining efficient operations.
D. Intelligent Transportation Systems: FOSCs are used in traffic management, toll collection, and public transportation systems, where real-time communication and monitoring are vital for safety and efficiency.
E. Utility Networks: Power and water utilities rely on FOSCs for protecting fiber optic splices in their monitoring and control systems, ensuring reliable service delivery and efficient resource management.
F. Military Communication Systems: In secure military networks, Optical Splice Closure safeguards fiber optic splices, enabling secure and reliable communication among different units and command centers.
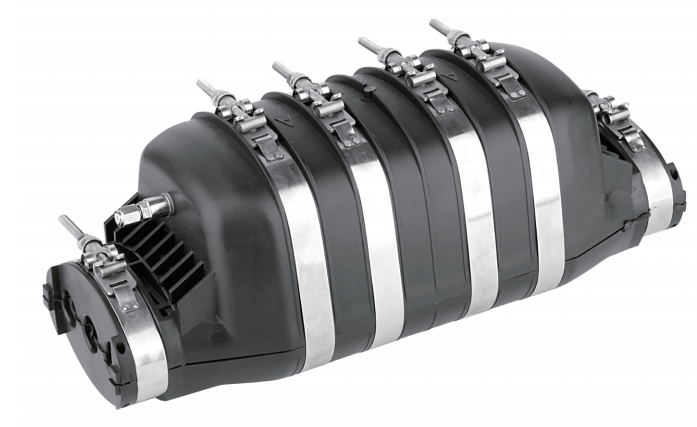

FOSC Installation, Maintenance, and Best Practices
Proper installation and maintenance of Closure Fiber Optic have a significant impact on the overall performance and reliability of an optical network:
A. Installation: Technicians should follow manufacturer guidelines and industry standards to ensure the integrity of the Fiber Joint Closure, including proper sealing, cable retention, and grounding. Using appropriate tools and equipment minimizes the risk of fiber damage during installation.
B.Maintenance: Regular inspections of Fiber Splice Box help verify their integrity, sealing, and grounding, allowing for timely maintenance to address any issues and ensure the network's continued performance.
Practices for FOSC selection and deployment:
A. Analyzing requirements: Assess the network's technical specifications, such as the number of fibers, cable types, and splice methods. Consider environmental factors like temperature, humidity, and potential exposure to water or dust.
B. Choose a reputable manufacturer: Select FOSCs from manufacturers with a proven quality and reliability track record. Look for certifications like IP68 (Ingress Protection) ratings, indicating the Fiber Optic Splice Closure's resistance to dust and water.
C. Planning for future growth: Choose FOSCs with modular or scalable designs to accommodate potential capacity expansions or network upgrades.
D. Training: Ensure technicians responsible for Optical Fiber Closure installation and maintenance are adequately trained and familiar with the manufacturer's guidelines, industry standards, and best practices.
FOSCs Trends and Innovations
As the demand for high-speed data transmission grows and 5G optical networks developed, Closure Fiber Optic must adapt to new technologies and requirements:
A. Large Capacity Closures: With increasing fiber density in networks, Fiber Splice Box will need to accommodate higher fiber counts while maintaining manageability and organization.
B. Improved FOSCs sealing and materials: Developments in sealing technology and materials will enhance the durability and environmental resistance of FOSCs, further ensuring the protection of fiber optic splices.
C. Integration of smart features: Incorporating sensors and monitoring capabilities into FOSCs will enable real-time status checks and proactive maintenance, reducing network downtime and improving performance.
D. Environmental and energy efficiency: FOSCs will be designed with eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient features as sustainability becomes more important in the industry.
Conclusion
Fiber Optic Splice Closures play an important role in the components of FTTH Connection. By understanding their components, types, applications, best practices, and future trends, network operators and professionals can effectively manage their networks for optimal performance and reliability. As the demand for high-speed data transmission continues to grow, FOSCs will remain essential components of modern communication systems, further emphasizing their significance in the future of telecommunications and data transmission.
Publisher: Mjadom
Author: Andy