When you think of data traveling long distances, you think of fiber optic lines and cables and for good reason. These cables use light to transmit information and lose no signal. You might be wondering how that works and why they’re better than the old ways. By understanding the structure and science behind fiber optics you can appreciate the tech that keeps you connected. So what happens when light goes through these cables and why is it so fast?
Fiber Optics
Fiber optics is a technology that uses light to transmit data through thin strands of glass or plastic. Data traveling at the speed of light—literally! This has changed the way we communicate and share information over long distances. Fiber optic cables are made up of these thin fibers that carry data as light signals. These light signals are generated by lasers or light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and travel through the fiber optic cable for fast and efficient data transfer. Whether it’s internet, phone or TV services, fiber optics is the backbone of modern communication.
Fiber Optics Basics
Fiber optics changes how we transmit data by using light instead of electrical signals. You can send lots of information fast and long distances with light pulses.
At its heart fiber optics uses the principle of total internal reflection where light travels through a glass or plastic fiber and bounces off the walls and doesn’t lose signal. You get less interference and more bandwidth making it perfect for internet, phone and cable TV services.
Fiber optic cables are lighter and more flexible than copper wires so installation is easier. As you go online or stream videos you’re using this tech and getting faster speeds and more reliable connections that makes your online life better.
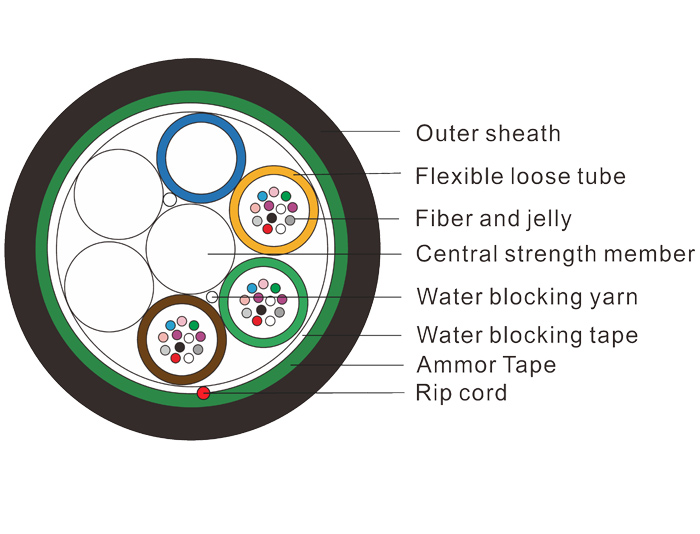
Fiber Optic Cables Structure
At the heart of fiber optic tech is the cable itself. The core of a fiber optic cable is super thin, often less than a tenth of a human hair.
You’ll see a fiber optic cable has three main parts: the core, the cladding and the outer jacket. The core is made of glass or plastic where light travels, the cladding surrounds it and reflects the light back into the core to prevent signal loss.
This design allows for data to be transmitted over long distances. The outer jacket protects the cable from environmental factors and physical damage.
Together these parts make a strong structure that enables fast communication. Understanding this structure is key as it’s the basis of how fiber optic cables work in transmitting information.
Fiber Optic Cable Components
A fiber optic cable is a work of art, made up of several parts that work together to transmit light signals. At the center of the cable is the core, a thin strand of optically pure glass or plastic where the light signals travel. The cladding surrounds the core and reflects the light back into the core to prevent signal loss. The coating around the cladding provides extra protection from physical damage. The outer jacket covers the whole assembly to protect from environmental factors, making the fiber optic cable strong and durable. Together these parts make a super efficient pipe for light signals to transmit data fast over long distances.
Light Transmission Principles
The structure of fiber optic cables is key to how they transmit a light beam. At the core the light beam travels through a thin glass or plastic fiber surrounded by a cladding layer that reflects the light beam back into the core.
This is based on the principle of total internal reflection. When the light beam hits the boundary between the core and cladding at a certain angle it bounces back instead of escaping. This allows the light beam to travel long distances with minimal loss.
You can think of it as a game of ping pong where the light beam bounces back and forth and maintains its strength as it travels through the cable. This is what makes fiber optics so good for communication.
Total Internal Reflection
Total internal reflection is the magic that makes fiber optic cables work. This happens when light hits the boundary between the core and cladding at a shallow angle and reflects back into the core instead of escaping. Think of it as a game of ping pong where the light bounces back and forth within the core and maintains its strength and direction. This continuous reflection allows light signals to travel long distances through the fiber optic cable with minimal loss. Thanks to total internal reflection fiber optics can transmit data fast and efficient making it the best choice for modern communication needs.
Fiber Optic Cables
When you get into fiber optic cables you’ll find two main types: single-mode and multi-mode.
Single-mode cables, also known as single mode cable, have a small core and only one light path and can transmit data long distances with minimal signal loss. They’re good for telecommunications and high speed internet.
Multi-mode cables have a larger core and multiple light paths and are good for shorter distances like within a building or campus. Although they’re generally cheaper and easier to install they have more signal attenuation.
Which one to choose depends on your needs, long range communication or internal networking solutions. Understanding the differences will help you make a informed decision.
Fiber Optic Cables Advantages
Fiber optic cables have several advantages over copper cables. First and foremost they have higher bandwidth and can transfer data faster. You can download, upload and stream content at lightning speed. Fiber optic cables are also immune to electromagnetic interference (EMI) so you have a stable and reliable connection even in areas with high electrical noise. Security is another big advantage; it’s very hard to tap into a fiber optic cable without being detected making it a more secure way of transmitting data. These advantages makes fiber optic cables the best choice for high speed, reliable and secure communication.
Fiber Optics Applications
Optical fiber technology changes the way we communicate and transmit data across industries.
You’ll find fiber optic cables in telecommunications for high speed internet and clear voice calls. In medical equipment for doctors to perform minimally invasive surgeries with precision through fiber optic endoscopes.
In broadcasting optical fiber technology delivers high definition video signals to enhance your viewing experience.
And in data centers to connect servers with fast data transfer rates. Businesses use optical fiber technology for secure and efficient data transmission.
You can also see them in smart cities where they support IoT devices and infrastructure management.
As technology advances optical fiber technology will only get bigger and make your world more connected and efficient than ever.
Fiber Optics in Computer Networks
Fiber optic cables are the backbone of modern computer networks, providing high speed and reliable data transmission between devices. They are used in local area networks (LANs), wide area networks (WANs) and metropolitan area networks (MANs) to ensure connectivity across different scales. In data centers and cloud computing applications fiber optics enable fast data transfer rates to support the massive data demands of today’s digital world. Whether it’s connecting servers, cloud services or high speed internet fiber optic cables are the backbone of modern computer networks for efficient and reliable communication.
FAQs
How do Fiber Optic Cables Compare to Copper Cables?
Fiber optic cables have faster data transmission and higher bandwidth than copper cables.
They’re also lighter, immune to electromagnetic interference and more reliable over long distances making them the better choice for modern communication systems.
Can Fiber Optic Cables be Damaged?
Yes, optical fibers can be damaged but they’re generally more durable than copper cables.
Handle them with care, avoid sharp bends or excessive pressure to prevent breaks and maintain signal quality.
How Long do Fiber Optic Cables Last?
Fiber optic lines usually last 20 to 30 years depending on the environment and usage.
Proper installation and maintenance can extend their life and ensure performance throughout their life.
Are Fiber Optic Installations Costly?
Yes, fiber optic installations are costly due to materials and labor.
But fiber optic technology gives long term savings through speed and reliability making it a good investment for many businesses and homes.
How do Weather Conditions Affect Fiber Optic Performance?
Fiber optic performance can be affected by weather conditions.
For example heavy rain or snow can cause signal attenuation and extreme temperatures can affect the cable’s physical properties.
Consider these factors for better connectivity.
Summary
In summary fibre optics change the way we transmit data with their innovative design and light transmission. By understanding how they work you can appreciate the speed and reliability they bring to telecommunications and internet services. Whether you’re streaming a video or making a call fibre optics are the backbone of it all. Embrace this technology and you’ll enjoy better digital experiences for years to come.
Publisher: Mjdom
Author: Andy